With the SolarWinds debacle fresh in our minds, we review the dramatic upsurge of cyberattack sophistication and equally spectacular cyber-vulnerability.
Remember how malware and the evolution of cyber-threats in the third and fourth quarters of 2020 made global news headlines?
In Q4, through monitoring over a billion sensors across multiple threat vectors around the world cybersecurity solutions firm McAfee Labs had observed an average of 648 threats per minute, an increase of 60 threats per minute (10%) over Q3.
Q3 and Q4 also saw COVID-19-related cyber-attack detections in the firm’s customer ecosystem increase by 240% in Q3 and 114% in Q4, while Powershell threats again surged 208% due to continued increases in Donoff malware activity.
Said its chief scientist and fellow Raj Samani said of the pandemic conditions prevailing at the time: “Though a large percentage of employees grew more proficient and productive in working remotely, enterprises endured more opportunistic COVID-19 related campaigns among a new cast of bad-actor schemes. Furthermore, ransomware and malware targeting vulnerabilities in work-related apps and processes were active and remain dangerous threats capable of taking over networks and data, while costing millions in assets and recovery costs.”
Five cyber-landscape takeaways
McAfee’s latest threats report has cited a 100% increase in vulnerabilities, a 43% increase in targeted attacks, and a 43% increase in malware, among trends. What else has the data uncovered about the ongoing cyber landscape?
- COVID-19-themed threats
The report cited a 605% increase in Q2, by another 240% in Q3, and a further 114% in Q4.
As organizations the world over adapted to unprecedented numbers of employees working from home, cybercriminals worked feverishly to launch COVID-19-themed attacks on a workforce coping with pandemic restrictions and the potential vulnerabilities of remote-device and bandwidth security. - Malware threats
In Q3 2020, the firm had observed an average of 588 threats per minute, an increase of 169 threats per minute (40%). By the fourth quarter, this average had risen to 648 threats per minute, an increase of 60 threats per minute (10%).
• Powershell threats grew 208% in Q4 driven largely by Donoff malware. There were numerous Powershell attacks utilizing Process Injection to insert code into legitimate running processes as a privilege escalation technique.
• Mobile malware grew 118% in Q4 in part due to a surge in SMS Reg samples.
The HiddenAds, Clicker, MoqHao, HiddenApp, Dropper and FakeApp strains were the most detected mobile malware families.
• Ransomware grew in 69% from Q3 to Q4 driven by Cryptodefense. REvil, Thanos, Ryuk, RansomeXX and Maze groups topped the overall list of ransomware families
• MacOS malware exploded in Q3 by 420% due to EvilQuest ransomware but then slowed towards the end of 2020 - Victims, vectors and vulnerabilities
— Publicly reported incidents in Q4: This was when thefirmtracked a 100% increase in publicly reported cyber incidents targeting the technology sector. Reported incidents in the public sector had grown by 93% over the same period in the previous year
— Attack vectors: In Q4, malware was the most reported cause of security incidents, followed by account hijackings, targeted attacks and vulnerabilities. Incidents related to new vulnerabilities had surged 100% in that quarter; malware and targeted attacks had each risen by 43%, and account hijackings by 30%
— Vulnerabilities exploited: Among the campaigns monitored and investigated, the Eternal Blue exploit was the most prominent in Q4 2020 - MITRE ATT&CK techniques
The top MITRE ATT&CK techniques observed in Q3 and Q4 included System Information Discovery, Obfuscated Files or Information, File and Directory Discovery, Data Encryption for Impact, Stop Services, Process Injection, Process Discovery, Masquerading Techniques, and Exploits of Public Facing Applications.
— System information discovery was one of the more notable MITRE techniques in the campaigns observed in Q4. The malware in these campaigns contained functionality that gathered the OS version, hardware configuration and hostname from a victim’s machine and communicated back to the threat actor.
— Obfuscated files or information was the second most observed technique for Q4. One noteworthy example was threat group APT28’s use of virtual hard drive (VHD) files to package and obfuscate their malicious payloads to bypass security technology.
— Process injection is aprivilege escalation technique found in several malware families and threat groups, including Powershell threats, RAT tools such as Remcos, ransomware groups such as REvil, and multiple state-sponsored APT groups.
— Exploits of public facing applications experienced a Q4uptick as multiple reports from CISA and NSA warned that state sponsored threat actors were actively leveraging several vulnerabilities in public facing applications such as remote management and VPN software. Beyond sophisticated nation-state actors, McAfee also observed ransomware groups leveraging this initial access tactic. - Attacks on cloud users
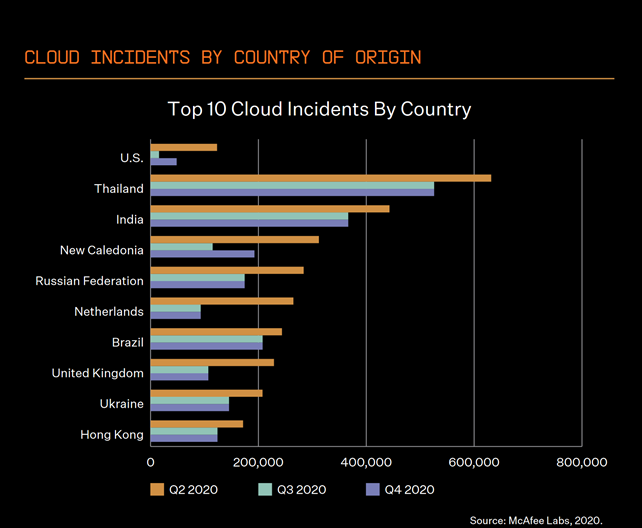
The report observed nearly 3.1 million external attacks on cloud user accounts. This is based on the aggregation and anonymization of cloud usage data from more than 30 million cloud users worldwide registered with the firm’s services during Q4 2020.
This data set represents companies in all major industries across the globe, including financial services, healthcare, public sector, education, retail, technology, manufacturing, energy, utilities, legal, real estate, transportation, and business services.
Finally, Thailand and Hong Kong have been ranked in the top 10 countries for suffering external attacks on cloud accounts. Comparatively, however, both countries’ Q3/Q4 figures are still lower than that of the cloud attacks in Q2, when COVID-19 helped to drive an all-time high for attacks across the world.