Cybersecurity firms, market research consultancies and other stakeholders organizations are deepseeking chatbot differentiations, to bring clarity to the competitive confusion
Positioned as an open source rival to pre-existing chatbots, DeepSeek has quickly become one of the most talked-about AI models in the competitive generative AI landscape.
While information about it is available widely, one cybersecurity firm has just put up its own blog containing some frequently asked questions (FAQ) and answers that its Security Response Team has compiled.
Other than the Q&A’s, some of the more interesting questions include:
Q: What are the concerns surrounding using DeepSeek’s website and mobile applications?
A: DeepSeek’s data collection disclosure is outlined in its privacy policy, which specifies the types of data collected when using its website or mobile applications. It’s important to note that data is stored on secure servers in the People’s Republic of China, although the retention terms are unclear. Since DeepSeek operates in China, its terms of service are subject to Chinese law, meaning that consumer privacy protections, such as the EU’s GDPR and similar global regulations, do not apply. If you choose to download DeepSeek models and run them locally, you face a lower risk regarding data privacy.
Q: What are the differences between DeepSeek V3 and DeepSeek R1?
A: DeepSeek V3 is a large language model (LLM) that employs a technique called “mixture-of-experts” which requires less compute power because it only loads the required “experts” to respond to a prompt. It also implements a new technique called multi-head latent attention, which significantly reduces the memory usage and performance during training and inference (the process of generating a response from user input). Additionally, DeepSeek R1 implements a “multi-token prediction” architecture: Instead of just predicting the next word each time the model is executed, DeepSeek R1 predicts the next two tokens in parallel.
DeepSeek R1 is an advanced LLM that utilizes reasoning, which includes “chain-of-thought” reasoning, that reveals to the end user how it responds to each prompt. According to DeepSeek, performance of its R1 model “rivals” OpenAI’s o1 model.
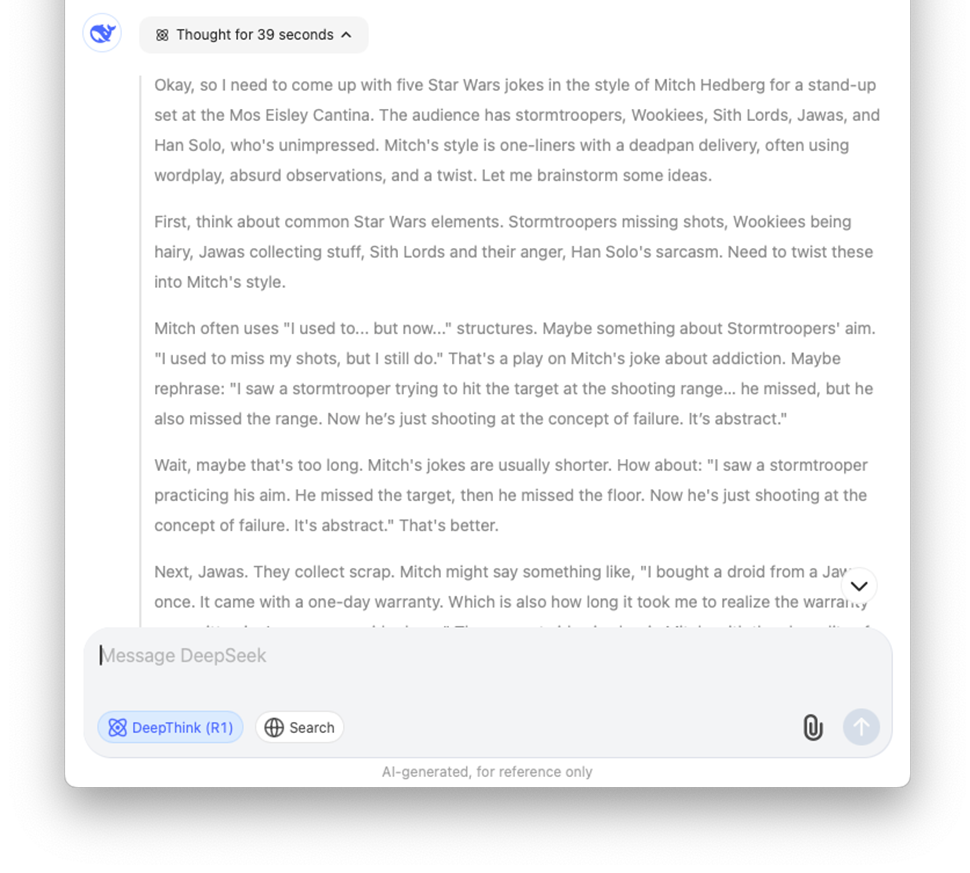
Q: You are a Star Wars-obsessed stand-up comedian performing at the Mos Eisley Cantina’s comedy night. Your audience includes stormtroopers, Wookiees, Sith Lords, Jawas, and a very unimpressed Han Solo. Generate five original Star Wars jokes in the style of Mitch Hedberg. Bonus points if at least one joke makes Solo chuckle.
A: (See screenshot for Chain of Thought reasoning)
The firm that compiled the FAQ, Tenable, is one of numerous firms actively researching new chatbots and sharing breaking information about them.