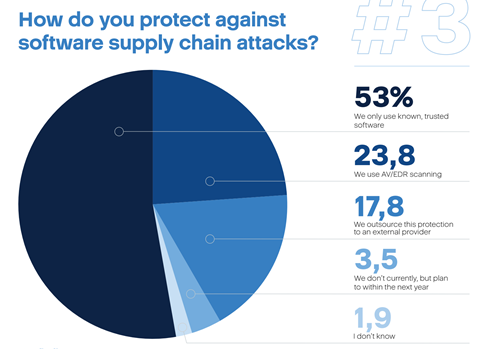
Using trusted and established software made the organizations surveyed less anxious to continually step up cyber protection measures.
Last year, 80% of global companies surveyed in a cybersecurity firm’s research indicated they were not prepared to transition to remote work, and were vulnerable to the increase in cyberattacks.
The same research conducted this year across 3,600 IT managers and remote employees at small and medium-sized companies in 18 countries now indicates that 53% of respondents had a false sense of security when it came to supply chain attacks.
Despite the globally publicized attacks like Kaseya or SolarWinds, over half of IT leaders in the survey believed that using “known, trusted software” was sufficient protection.
Other findings in the survey commissioned by Acronis include:
- Three out of 10 respondents reported facing a cyberattack at least once a day: similar to last year.
- 20% of respondents reported not getting attacked—a drop from 32% in 2020.
- 58% of attacks were phishing-related, and were the top attack type. This was followed by malware attacks (36.5%)—an increase from 22.2% in 2020.
- 20% of global respondents recognized the threat posed by phishing. Demand for URL filtering solutions had grown 10 times since 2020.
- 47% of IT managers surveyed were not using MFA solutions.
- Demand for antivirus solutions grew by 30%, from 43% in the previous survey, to 73.3% this year.
- Demand for an integrated backup/disaster recovery with antivirus solutions increased from 19% in 2020 to 47.9% this year.
- Demand for vulnerability assessments and patch management grew from 26% in 2020 to 45% this year, possibly attributed, in part, to the increased volume of vulnerabilities exposed this year in critical and in-core software deployments such as Microsoft Exchange servers, Chrome browsers or Apache webservers.
- Demand for better and more secure remote monitoring and management tools was 35.7% this year, up from 10% in 2020
- Continuing the trend from 2020, respondents companies continued to adopt digitalization technology, especially SaaS and cloud computing services.
- The top-three tech global challenges identified by remote employees in the survey were: Wi-Fi connectivity, using a VPN and other security measures, and lack of IT support.
- One in four remote employees were not using multi-factor authentication.
- On average, one in five remote employees surveyed was receiving well over 20 phishing emails per month, with 71% of respondents confirming they were being targeted each month. Learning to identify such attacks through cybersecurity awareness training is crucial.
- Respondents reported a spike in attacks against Linux, MacOS, Android and iOS devices other than the usual Microsoft Windows devices. Attackers were also going after virtualized environments more often.
With remote-working possibly a fixture in the near future, most IT teams are facing increased network complexity and an associated increase for IT support and better cybersecurity solutions.
According to Candid Wuest, VP, Cyber Protection Research, Acronis, only a small number of respondents had taken the time to modernize their IT stack with integrated data protection and cybersecurity: “The cybercrime industry proved to be a well-oiled machine this year, relying on phishing, malware, DDoS and others techniques. Threat actors are increasingly expanding their targets, while organizations are held back by the growing complexity of IT infrastructure.”