PowerShell-based malware surged 117% due to malicious Donoff documents, and there were 7.5m attacks on Cloud users.
In Q2 this year, the team at McAfee saw an average of 419 new threats per minute, with overall new malware samples growing by 11.5%.
A significant proliferation in malicious Donoff Microsoft Office document attacks propelled new PowerShell malware up 117%, and cybercriminals continuing to lure victims with pandemic themes and exploiting security lapses in remote-work protocols.
According to the firm’s chief scientist and fellow Raj Samani, what began as a trickle of phishing campaigns and the occasional malicious app quickly turned into a deluge of malicious URLs, attacks on cloud users, and capable threat actors “leveraging the world’s thirst for more information on the coronavirus pandemic as an entry mechanism into systems across the globe.”
- Pandemic-themed threats
After a first quarter that saw the world plunge into pandemic, the second quarter saw enterprises continuing to adapt to unprecedented numbers of employees working from home and dealing with the associated cybersecurity challenges.
Bad actors retargeted increasingly-sophisticated techniques toward businesses, governments, schools, and workforces coped with lockdown restrictions and potential vulnerabilities of remote-working and bandwidth security issues.
In Q2, McAfee’s global network of over a billion sensors observed a 605% increase in pandemic-related attack detections compared to Q1.
- Donoff and PowerShell malware
Donoff played a critical role in driving the 689% surge in PowerShell malware in Q1 2020.
The infected Microsoft Office documents act as TrojanDownloaders by leveraging the Windows Command shell to launch PowerShell and proceed to download and execute malicious files.
In Q2, the acceleration of Donoff-related malware growth slowed but remained robust, driving up PowerShell malware by 117% and helping to drive a 103% increase in overall new Microsoft Office malware.
This activity should be viewed within the context of the overall continued growth trend in PowerShell threats. In 2019, total samples of PowerShell malware grew 1,902%.
- Cloud attacks
Q2 saw nearly 7.5 million external attacks on cloud user accounts. This was based on the aggregation and anonymization of cloud usage data from more than 30 million McAfee cloud users worldwide during the reporting period.
This data set represents companies in all major industries across the globe, including financial services, healthcare, public sector, education, retail, technology, manufacturing, energy, utilities, legal, real estate, transportation, and business services.
Q2 threat summary
- Malware overview
The firm’s global sensors detected 419 new threats per minute in Q2 2020, an increase of almost 12% over the previous quarter. Ransomware growth remained steady compared to Q1 2020’s numbers. - New coin-miners
After growing 26% in Q1, new coin-mining malware increased 25% over the previous quarter sustained by the popularity of new coin-mining applications. - Mobile malware overview
After a 71% increase in new mobile malware samples in Q1, Q2 saw the category slow 15% despite a surge in Android Mobby Adware. - IoT overview
New IoT malware increased only 7% in Q2, but the space saw significant activity by Gafgyt and Mirai threats, both of which drove growth in new Linux malware by 22% during the period. - Regional cyber-activity
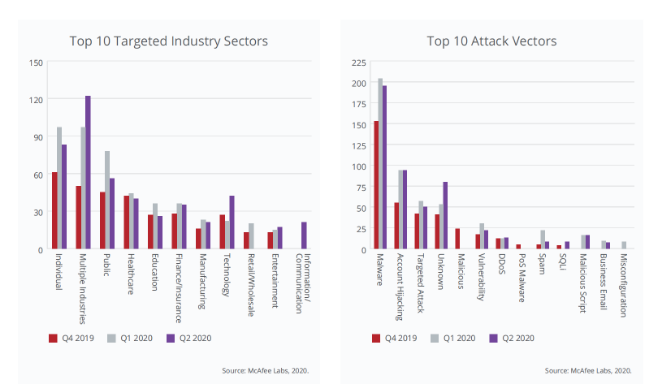
McAfee counted 561 publicly-disclosed security incidents in Q2 2020, an increase of 22% from Q1. Disclosed incidents targeting North America decreased 30% over the previous quarter. These incidents decreased 47% in the United States, but increased 25% in Canada and 29% in the United Kingdom. - Attack vectors overview
Overall, malware led among reported attack vectors, accounting for 35% of publicly-reported incidents in Q2. Account hijacking and targeted attacks accounted for 17% and 9% respectively.
Finally, disclosed incidents detected in the second quarter targeting science and technology increased 91% over the previous quarter. Incidents in manufacturing increased 10%, but public sector events decreased by 14%.