Ransomware and IIoT vulnerabilities are also cyber threats to watch for this year, reports one cybersecurity solutions firm.
In the first half of this year, COVID-19-related cyber threats were the single largest type of threat encountered by cybersecurity specialist Trend Micro wherein nearly 92% of these threats were email-based.
More than 37,700 cases were detected from Hong Kong, of which more than 25,000 were email-based threats. The risk to businesses was compounded by security gaps created by the huge shift to a remote workforce.
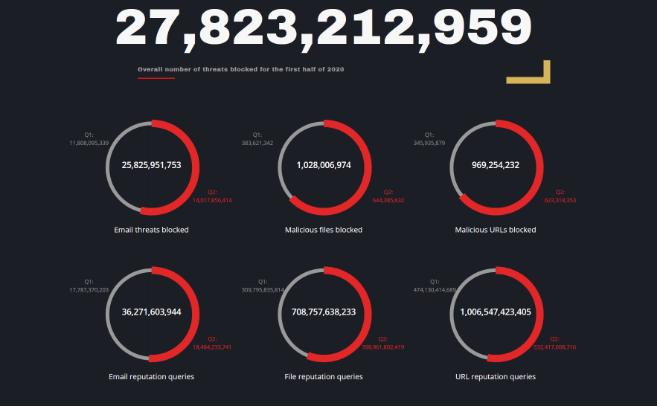
In total, Trend Micro reports blocking 27.8 billion cyber threats in the first half of 2020, 93% of which were email-borne. Business Email Compromise (BEC) detections had increased by 19% from the second half of 2019, in part due to scammers trying to capitalize on home workers being more exposed to social engineering.
Ransomware is a constant spectre in 2020. There has been a 45% increase in new ransomware families since 2019, and a 16% increase in vulnerabilities disclosed in industrial control systems, which could create major challenges for smart factory owners and other IIoT environments.
Around the world, organizations have also been burdened by a significant spike in newly-disclosed vulnerabilities. Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative (ZDI) published a total of 786 advisories, representing a 74% increase from the situation in H2 2019. Some of these came as part of Microsoft Patch Tuesday updates, which have fixed an average of 103 CVEs per month so far in 2020—including the largest number of patches ever issued in a single month (129) in June.
Said Tony Lee, Consulting Manager of Trend Micro Hong Kong and Macau: “IT leaders must continue to adapt their cybersecurity strategies to account for increased threats. That means protecting remote endpoints, cloud systems, user credentials and VPN systems, as well as refreshing training courses to turn that newly-dispersed workforce into a more effective first line of defense.”

















