Newly-created accounts suffered the highest attack rate in that time period, for credential stuffing in streaming services, gaming and gambling sites.
Guess which age groups were most vulnerable to fraud attacks in H2 2020: young (<25) or older adults (>70)?
Answer: BOTH!
According to data from LexisNexis Risk Solutions’ report on that period, the under-25 age group was most vulnerable to fraud attacks; the oldest age group was second-most vulnerable and lost the most money. The stark risk at both ends of the age spectrum emphasizes the importance for companies to protect both new-to-digital and vulnerable customers when transacting online in 2021.
The report is the result of analyses of transaction data from the firm’s Digital Identity Network, a repository of global shared intelligence gained from billions of consumer interactions including logins, payments and new account applications amounting to around 47.1 billion transactions in 2020.
The fraud attack rate observed in the ecosystem had decreased on average across all digital businesses year-over-year, although media companies saw an increase in the overall attack rate at account opening.
An evolving cyberthreat landscape
According to the data, malicious attack vectors persisted despite reduced attack rates recorded across businesses as automated bot attacks offered fraudsters a cheap, quick and effective method of initial attack. The 24.6 billion transactions between July through December 2020 showed that mass automated bots used to test identity credentials remained widespread.
The firm’s ecosystem also recorded bot attacks across global regions and within a wide variety of industries and use cases. Likewise, new account creations continued to see high attack rates, representing a key point of entry for fraudsters looking to monetize credentials harvested from data breaches.
Other findings include:
- Human-initiated attacks dropped, bot attacks increased: The former type of attacks in 2020 dropped by roughly 184 million while the number of bot attacks grew by 100 million in the whole of 2020. In both cases, the largest number of fraud attacks by volume originated from fraudsters located in the US, with countries like Canada, the UK and Germany also fitting into the top 10 countries for each attack method. Growth economies increasingly contributed to the number of fraud attacks, with rises in human-initiated attacks originating from Guatemala, Bahrain and ,Zimbabwe and a larger number of bot attacks coming from the Isle of Man, United Arab Emirates and Nigeria.
67% of all transactions were via mobile channels, with much of the transaction growth coming from trusted customers.
- H2 2020 cybercrime victim age profiles: With many new-to-digital customers coming online for the first time, the youngest age group of online users (under 25s) were found to be the most susceptible to fraud attacks in H2. There was a 10% growth in this age group in the digital identity network ecosystem.
The oldest age group (>75) had experienced the next-highest attack rate. This group generally had less familiarity with the latest digital technologies and were more susceptible to scams and phishing attempts. While millennials and Gen Z were most susceptible to fraud attacks, the average fraud loss per customer increased progressively with age, likely influenced by larger disposable incomes later in life.
The paradox of why fraudsters choose to target the younger age group in proportionally higher volumes is perhaps explained by the fact that higher success rates can offset lower monetary gains.
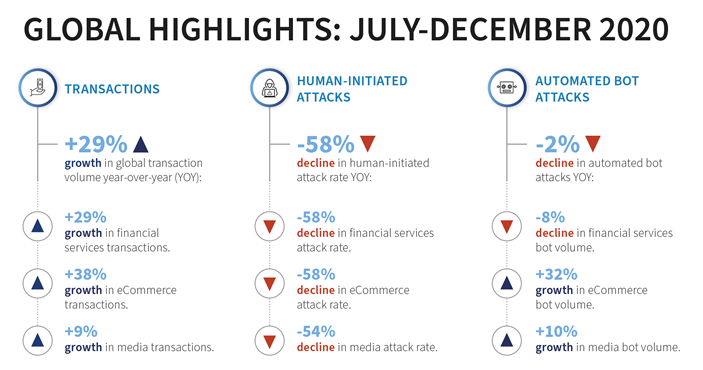
- H2 2020 industry-level cybercrime landscape: The firm’s Digital Identity Network found a 29% growth in global transaction volume in H2 2020 compared on year. This growth came in the financial services (29%), e-commerce (38%) and media (9%) sectors.
Financial services saw low overall attack rates, driven by a high volume of repeat login transactions from trusted customers, with the exception of payment transactions, which saw attacks at a higher rate than any other industry. This presented a key opportunity for fraudsters to cash out.
E-commerce saw the largest growth in bot volume in comparison to other industries. The 2.7% attack rate for mobile app e-commerce payments was higher than any other industry. This represents an evident point of risk for these businesses.
New account creations for media companies were attacked at a higher rate than any other industry, with fraudsters often using media organizations like streaming services, gaming and gambling sites and apps to test stolen identity data.
Commented Rebekah Moody, Director of Fraud and Identity, LexisNexis Risk Solutions: “Cybercriminals are opportunists first and masters of disguise second. They are always on the lookout for a new target whether this involves new lines of credit, new online businesses or new-to-digital consumers. While digital businesses are working hard to better provide for new and existing customers, they must identify and mitigate potential risks moment by moment in order to protect consumers from becoming victims of fraud.”
Moody said building a layered defense is key. Uniting the best digital identity intelligence with physical identity solutions and behavioral biometrics intelligence can be the game changer that organizations need to lessen the unpredictable tides of fraud: “Digital identity intelligence in particular is crucial for businesses to understand the behavior, transaction history and device intelligence of each identity entering their environment. When we can crowdsource real time intelligence across global digital businesses, it offers an unparalleled view of trust and risk. This creates a low-friction online experience because businesses can better recognize trusted, returning consumers.”
Moody will be reviewing the H2 2020 data in a global webinar on March 23, 2021.

















